International Day of Yoga, or commonly, is celebrated annually on 21 June since its inception in 2015. An international day for yoga was declared unanimously by the United Nations General Assembly (UNGA). Yoga is a physical, mental and spiritual practice originated in India. The Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi in his UN address suggested the date of 21 June, as it is the longest day of the year in the Northern Hemisphere and shares a special significance in many parts of the world. He stated:
Yoga is an invaluable gift of India’s ancient tradition. It embodies unity of mind and body; thought and action; restraint and fulfilment; harmony between man and nature; a holistic approach to health and well-being. It is not about exercise but to discover the sense of oneness with yourself, the world and the nature. By changing our lifestyle and creating consciousness, it can help in well being. Let us work towards adopting an International Yoga Day.
— Narendra Modi, UN General Assembly
A brief history of Yoga:
Yoga is considered to be an ancient practice which was originated in our country. The practice is considered to be almost 5000 years old. Yoga was developed as a way to achieve harmony and balance between the heart and soul and to achieve divine enlightenment. Not only this, with time passing by, it was also seen that the practice of yoga had and still have medical benefits. It helps in curing many diseases like diabetes and high blood pressure and alleviating physical injuries and chronic pain. It has been practiced in India for centuries and now Yoga has also found its way in the western world. In recent decades Yoga became really popular outside of India and many other cultures have embodied yoga in them.
Is yoga a religion?
People say that yoga is Hindu, but “Hinduism” is a problematic term, coined by outsiders for everything they saw going on in India. Yoga stems from the Vedas – the Indian holy texts that were composed from around 1900BC. Besides yoga, three major religions came from those texts – Hinduism, Jainism and Buddhism
So do not get carried away by people propagating Yoga as a religion. Yoga is a mind and body practice, various styles of yoga combine physical postures, breathing techniques, and meditation or relaxation. Yoga is well known for its postures and poses, but they were not a key part of original yoga traditions in India. Fitness was not a primary goal. Practitioners and followers of yogic tradition focused instead on other practices, such as expanding spiritual energy using breathing methods and mental focus.
Need a Yoga therapy to heal your body mind and soul? then get in touch with Dr. Desai’s Clinic with professional Ayurvedic Doctor in Goa offering many treatment including Yoga therapy in Goa and more.
Philosophy
To convey its spiritual message and guide sessions, yoga often uses the imagery of a tree with roots, a trunk, branches, blossoms, and fruits. Each “branch” of yoga represents a different focus and set of characteristics.

The six branches are:
- Hatha yoga: This is the physical and mental branch designed to prime the body and mind.
- Raja yoga: This branch involves meditation and strict adherence to a series of disciplinary steps known as the “eight limbs” of yoga.
- Karma yoga: This is a path of service that aims to create a future free from negativity and selfishness.
- Bhakti yoga: This aims to establish the path of devotion, a positive way to channel emotions and cultivate acceptance and tolerance.
- Jnana yoga: This branch of yoga is about wisdom, the path of the scholar, and developing the intellect through study.
- Tantra yoga: This is the pathway of ritual, ceremony, or consummation of a relationship.
Approaching yoga with a specific goal in mind can help a person decide which branch to follow.
Physical benefits of yoga –
- increased flexibility.
- increased muscle strength and tone.
- improved respiration, energy and vitality.
- maintaining a balanced metabolism.
- weight reduction.
- cardio and circulatory health.
- improved athletic performance.
- protection from injury.
Chakras
The word “chakra” literally means spinning wheel.
Yoga maintains that chakras are center points of energy, thoughts, feelings, and the physical body. According to yogic teachers, chakras determine the way people experience reality through emotional reactions, desires or aversions, levels of confidence or fear, and even physical symptoms and effects.
When energy becomes blocked in a chakra, it is said to trigger physical, mental, or emotional imbalances that manifest in symptoms, such as anxiety, lethargy, or poor digestion.
Asanas are the physical positions in Hatha yoga. People who practice yoga use asanas to free energy and stimulate an imbalanced chakra.
There are seven major chakras, each with their own focus:
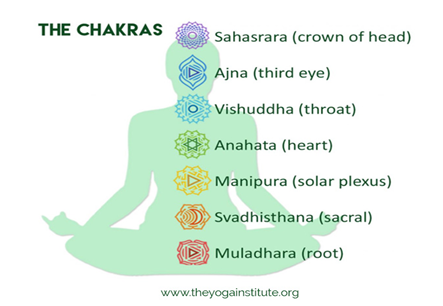
- Sahasrara: The “thousand-petaled” or “crown” chakra represents the state of pure consciousness. This chakra is located at the crown of the head, and the color white or violet represents it. Sahasrara involves matters of inner wisdom and physical death.
- Ajna: The “command” or “third-eye chakra” is a meeting point between two important energetic streams in the body. Ajna corresponds to the colors violet, indigo, or deep blue, though traditional yoga practitioners describe it as white. The ajna chakra relates to the pituitary gland, which drives growth and development.
- Vishuddha: The color red or blue represents the “especially pure” or “throat” chakra. Practitioners consider this chakra to be the home of speech, hearing, and metabolism.
- Anahata: The “unstruck” or “heart” chakra relates to the colors green and pink. Key issues involving anahata include complex emotions, compassion, tenderness, unconditional love, equilibrium, rejection, and wellbeing.
- Manipura: Yellow represents the “jewel city” or “navel” chakra. Practitioners connect this chakra with the digestive system, as well as personal power, fear, anxiety, developing opinions, and tendencies towards an introverted personality.
- Svadhishthana: Practitioners claim that the “one’s own base” or “pelvic” chakra is the home of the reproductive organs, the genitourinary system, and the adrenal gland.
- Muladhara: The “root support” or “root chakra” is at the base of the spine in the coccygeal region. It is said to contain our natural urges relating to food, sleep, sex, and survival, as well as the source of avoidance and fear.
Types
Modern yoga has a range of styles to suit everyone, whatever the desired outcome. Modern yoga has evolved with a focus on exercise, strength, flexibility, and breathing. It can help boost physical and mental well-being.
There are many styles of yoga, and no style is more authentic or superior to another. The key is to choose a class appropriate for your fitness level.
Types and styles of yoga may include:
- Ashtanga yoga: This type of yoga uses ancient yoga teachings. However, it became popular during the 1970s. Ashtanga applies six established sequences of postures that rapidly link every movement to breath.
- Bikram yoga: Also known as “hot” yoga, Bikram occurs in artificially heated rooms at temperatures of nearly 105 degrees and 40 percent humidity. It consists of 26 poses and a sequence of two breathing exercises.
- Hatha yoga: This is a generic term for any type of yoga that teaches physical postures. “Hatha” classes usually serve as a gentle introduction to the basic yoga postures.
- Iyengar yoga: This type focuses on finding the correct alignment in each pose using a range of props, such as blocks, blankets, straps, chairs, and bolsters.
- Jivamukti yoga: Jivamukti means “liberation while living.” This type emerged in 1984 and incorporates spiritual teachings and practices that focus on the fast-paced flow between poses rather than the poses themselves.This focus is called vinyasa. Each class has a theme, which is explored through yoga scripture, chanting, meditation, asana, pranayama, and music. Jivamukti yoga can be physically intense.
- Kripalu yoga: This type teaches practitioners to know, accept, and learn from the body. A student of Kripalu learns to find their own level of practice by looking inward. The classes usually begin with breathing exercises and gentle stretches, followed by a series of individual poses and final relaxation.
- Kundalini yoga: Kundalini means “coiled, like a snake.” Kundalini yoga is a system of meditation that aims to release pent-up energy.A class typically begins with chanting and ends with singing. In between, it features asana, pranayama, and meditation customized to create a specific outcome.
- Power yoga: In the late 1980s, practitioners developed this active and athletic type of yoga, based on the traditional ashtanga system.
- Sivananda: This is a system based on a five-point philosophy. This philosophy maintains that proper breathing, relaxation, diet, exercise, and positive thinking work together to form a healthy yogic lifestyle. Typically uses the same 12 basic asanas, bookended by sun salutations and savasana poses.
- Viniyoga: Viniyoga can adapt to any person, regardless of physical ability. Viniyoga teachers require in-depth training and tend to be experts on anatomy and yoga therapy.
- Yin: This is a quiet, meditative yoga practice, also called taoist yoga. Yin yoga allows the release of tension in key joints, including: the ankles, knees, hips, the whole back, neck, shoulders. Yin poses are passive, meaning that gravity shoulders most of the force and effort. Prenatal yoga: Prenatal yoga uses postures that practitioners have designed for people who are pregnant. It can support people in getting back into shape after pregnancy as well as supporting health during pregnancy.
- Restorative yoga: This is a relaxing method of yoga. A person spends a restorative yoga class in four or five simple poses, using props like blankets and bolsters to sink into deep relaxation without exerting any effort in holding the pose.
Risks and side effects
Yoga is low-impact and safe for people when a well-trained instructor is guiding the practice.
Injury due to yoga is an infrequent barrier to continued practice, and severe injury due to yoga is rare. However, consider a few factors before starting.
Anyone who is pregnant or who has an on-going medical condition, such as high blood pressure, glaucoma, or sciatica, should talk to their healthcare practitioner before practicing yoga. They may need to alter or avoid some yoga poses.
Beginners should avoid extreme poses and difficult techniques, such as headstand, lotus position, and forceful breathing.
When using yoga to manage a condition, do not replace medical care with yoga or postpone seeing a healthcare provider about pain or any other medical problem.
There are many different types of yoga depending on what people want from it and a person’s current level of physical fitness. However, some people choose to replace conventional treatment for conditions with yoga and this can prevent a person from receiving the necessary care.
People with certain conditions, such as sciatica, should approach yoga slowly and with caution.
Yoga can help support a balanced, active lifestyle.
“Anyone who can breathe can benefit from yoga. Breath is a portal to peace, relaxation and life force, which we can access at all times. Yoga is ancient wisdom for a modern world: yoking body, mind and spirit to the Universal.
Yoga is not about shape of your body, but the shape of one’s life”.
This International Yoga day 2019 theme is Climate Action; it’s time we all wake up to the adverse call of nature. It’s high time we take act at our level to save our lovely planet, before we get buried and extinct like dinosaurs. Let’s not just celebrate Yoga day, but also believe and stay true to the meaning of the term YOGA – meaning to unite/join; union of body and consciousness.

